Firefox Browser Global Proxy
In this area, you can change the proxy configuration.
Menu path: Sessions > Firefox Browser > Firefox Browser Global > Proxy
To change the proxy configuration, proceed as follows:
In the Proxy Configuration pull-down menu, select the type of proxy configuration.
The following proxy configurations are available:Direct connection to the Internet (Default)
Manual proxy configuration
Automatic proxy configuration
System-wide proxy configuration
Auto-detect proxy settings for this network
Enter the necessary configuration data for the selected proxy configuration.
Direct Connection to the Internet
With this proxy configuration, no proxy is used.
Manual Proxy Configuration
The configuration data must be specified in the following fields.
FTP proxy: URL of the proxy for FTP
Port: Port of the proxy for FTP
HTTP proxy: URL of the proxy for HTTP
Port: Port of the proxy for HTTP
SSL proxy: URL of the proxy for SSL
Port: Port of the proxy for SSL
SOCKS host: URL of the proxy for SOCKS
Port: Port of the proxy for SOCKS
SOCKS protocol version: Version of the SOCKS protocol used (default: SOCKS v5)
No proxy for: List of URLs for which no proxy is to be used (default: localhost, 127.0.0.1)
Proxy realm: Area in which the browser authenticates itself for the proxy. Together with the user name and password, this information is necessary for authentication.
The Proxy realm field is internally pre-populated with the value moz-proxy://[HTTP Proxy]:[Port]. If the field is empty, this value will be used when authenticating the browser. If the proxy expects another unknown value for the proxy realm, you can determine this as follows: Leave the User name and Password fields empty and launch the browser. The dialog window which appears will contain the correct value for the Proxy realm field:
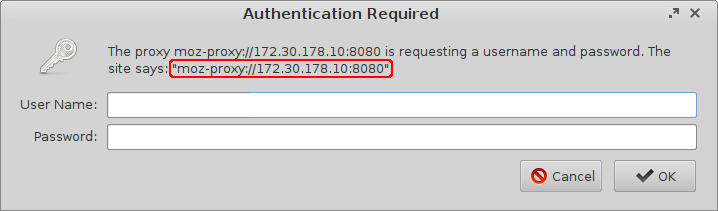
In the example above, the value for the Proxy realm field is as follows: moz-proxy://172.30.178.10:8080
Use passthrough authentication: This option can be used if the local thin client logon takes place via Kerberos.
☑ The logon information saved temporarily when logging on to the thin client will be carried over when logging on to the proxy.
User name: User name with which the browser authenticates itself for the proxy.
Password: Password with which the browser authenticates itself for the proxy.
Do not prompt for proxy authentication if credentials are saved
☑ If logon data are already saved in the browser, the user will not be asked for a user name and password. (default)
This option should not be enabled in multiuser environments. If this option is enabled in a multiuser environment, a user can use the logon data of a previous user.
Automatic Proxy Configuration
With this proxy configuration, the PAC file (Proxy Auto Config) available under URL will be used.
URL: URL of the proxy configuration file
Do not prompt for proxy authentication if credentials are saved
☑ If logon data are already saved in the browser, the user will not be asked for a user name and password. (default)
This option should not be enabled in multiuser environments. If this option is enabled in a multiuser environment, a user can use the logon data of a previous user.
System-Wide Proxy Configuration
With this proxy configuration, the proxy configured under Setup > Network > Proxy will be used.
Do not prompt for proxy authentication if credentials are saved
☑ If logon data are already saved in the browser, the user will not be asked for a user name and password. (default)
This option should not be enabled in multiuser environments. If this option is enabled in a multiuser environment, a user can use the logon data of a previous user.
Auto-Detect Proxy Settings for This Network
With this proxy configuration, WPAD (Web Proxy Autodiscovery Protocol) will be used. The browser will determine the URL of the WPAD file wpad.dat automatically with the help of DNS.
Do not prompt for proxy authentication if credentials are saved
☑ If logon data are already saved in the browser, the user will not be asked for a user name and password. (default)
This option should not be enabled in multiuser environments. If this option is enabled in a multiuser environment, a user can use the logon data of a previous user.
