Windows Drive
Menu path: Setup > Network > Network Drives > Windows Drive
In this area, you can integrate network drives shared by Windows as well as those from Linux/Unix servers via the SMB protocol (Samba).
You can find a sample configuration at the end of this page.
To manage the drive list, proceed as follows:
Click
 to create a new entry.
to create a new entry.Click
 to remove the selected entry.
to remove the selected entry.Click
 to edit the selected entry.
to edit the selected entry.Click
 to copy the selected entry.
to copy the selected entry.
Clicking ![]() will bring up the Add dialogue, where you can define the following settings:
will bring up the Add dialogue, where you can define the following settings:
Enabled: Defines whether the configuration entry will be applied.
☑ The network drive will be integrated.
Local Mount Point: The local directory under which the server directory is to be visible (default:
/smbmount)Server: The IP address, Fully-Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) or NetBIOS name of the server.
Share Name: Path name as exported by the Windows or Unix Samba host.
User name: User name for your user account on the Windows or Unix Samba host.
Password: Password for your user account on the Windows or Unix Samba host.
User writable
☑ The user can not only read but also write directory contents. Otherwise, only the local root user is able to do this.
☐ The user can only read directory contents. (default)
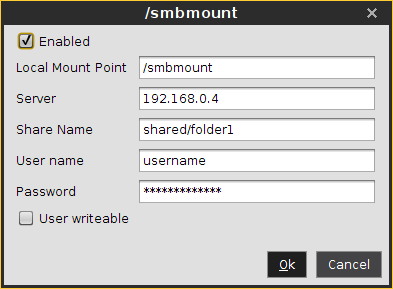
Sample configuration entry
The following picture shows a sample configuration entry.
If a NetBios name is provided for Server, make sure it is not preceded by slashes, e.g. \\myComputer (wrong) vs. myComputer (correct).
For Local Mount Point, only / (Linux/Unix-style forward slash) can be used as a path separator. Note that if you enter, for example, \smbmount as a moint point, a directory called \smbmount will be created, because \ is a legal character in Linux directory names. For Share Name, however, / (Linux/Unix-style forward slash) or \ (Windows-style backward slash) can be used as a path separator.