IGEL Cloud Gateway vs. Reverse Proxy for the Communication between UMS 12 and IGEL OS Devices
With the launch of IGEL Universal Management Suite (UMS) 12, the Unified Protocol used for all communication between the UMS and IGEL OS 12 devices was introduced, see Overview of the IGEL UMS . The Unified Protocol is a secure protocol that uses TCP 8443, see IGEL UMS Communication Ports . However, depending on the structure of your UMS environment, company's security policies, etc., it may be insufficient, and the use of the IGEL Cloud Gateway (ICG) or reverse proxy may be required. In the following article, you will find pros and cons of each solution.
In general UMS/ICG only needs routing for the configured web port between the device and the UMS/ICG. If any of the network components terminates SSL, the client cert needs to be forwarded in a HTTP header.
The example configurations in the pictures are for general illustrative purposes. Each network configuration will vary depending on the network setup, i.e. whether the UMS is in a DMZ or not.
Option 1: ICG 12
In the case of the ICG, endpoint devices connect to the ICG as well as the UMS connects to the ICG, see Devices and UMS Server Contacting Each Other via ICG. The WebSocket communication between the ICG and the UMS as well as between the ICG and the device is only established after mutual authentication, and the communication is encrypted with TLS. All data is routed through this WebSocket.
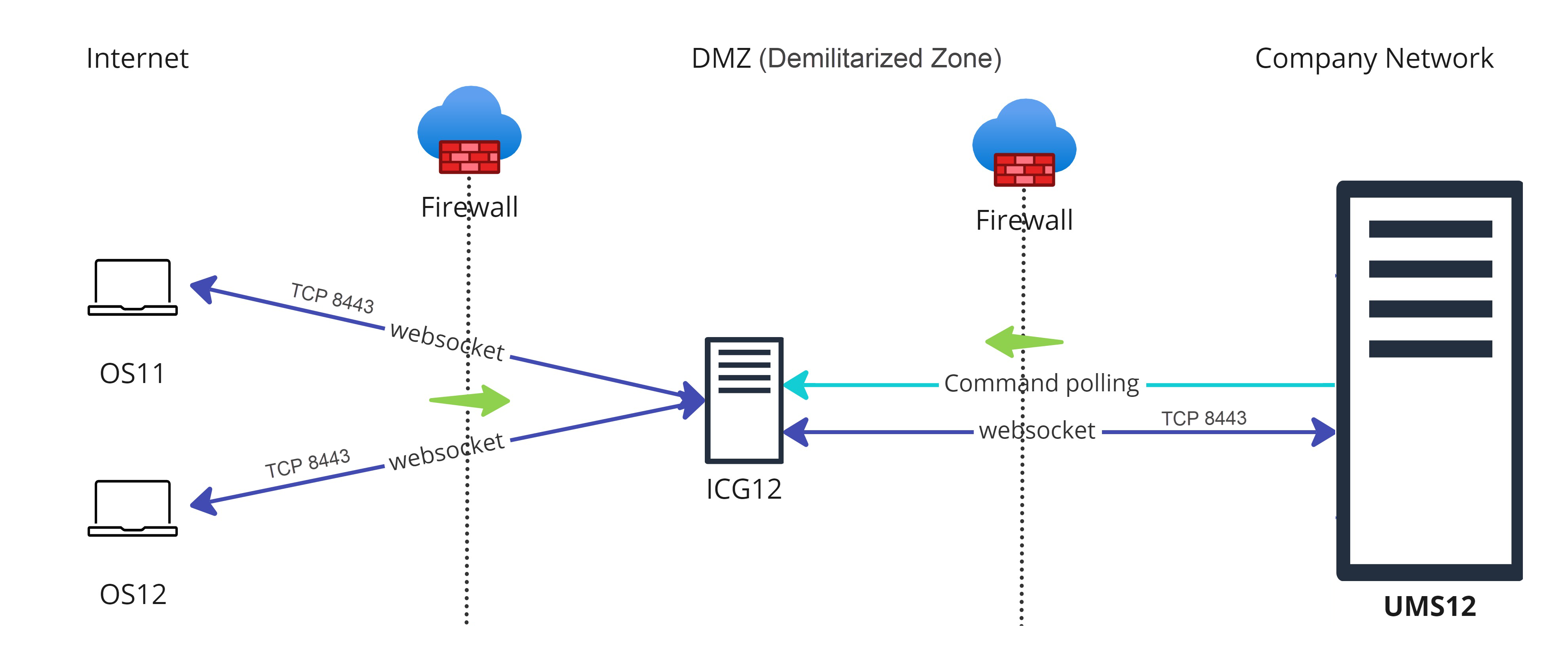
Legend to the image:
 : Shows that the traffic in the WebSocket runs in both directions.
: Shows that the traffic in the WebSocket runs in both directions. (multicolored): Shows from which side firewalls etc. must be opened.
(multicolored): Shows from which side firewalls etc. must be opened.
Advantages
Suitable for mixed environments when you manage both IGEL OS 12 and IGEL OS 11 devices.
No inbound connection from the device to the UMS.
Only the ICG is exposed to the Internet. Thus, if compromised, the UMS is NOT compromised at the same time.
Simple and lightweight, which minimizes the attack surface.
Disadvantages
UMS as an Update Proxy feature cannot currently be used, i.e. IGEL OS devices can download the apps from the App Portal only, not from the UMS Server. See Configuring Global Settings for the Update of IGEL OS Apps .
Higher latency and longer command execution in comparison to the reverse proxy. For large enterprise environments, the use of a reverse proxy may be considered.
Option 2: Reverse Proxy
Another possibility to route the traffic via port 8443 is to use a reverse proxy. The reverse proxy will forward the requests from devices to the UMS.
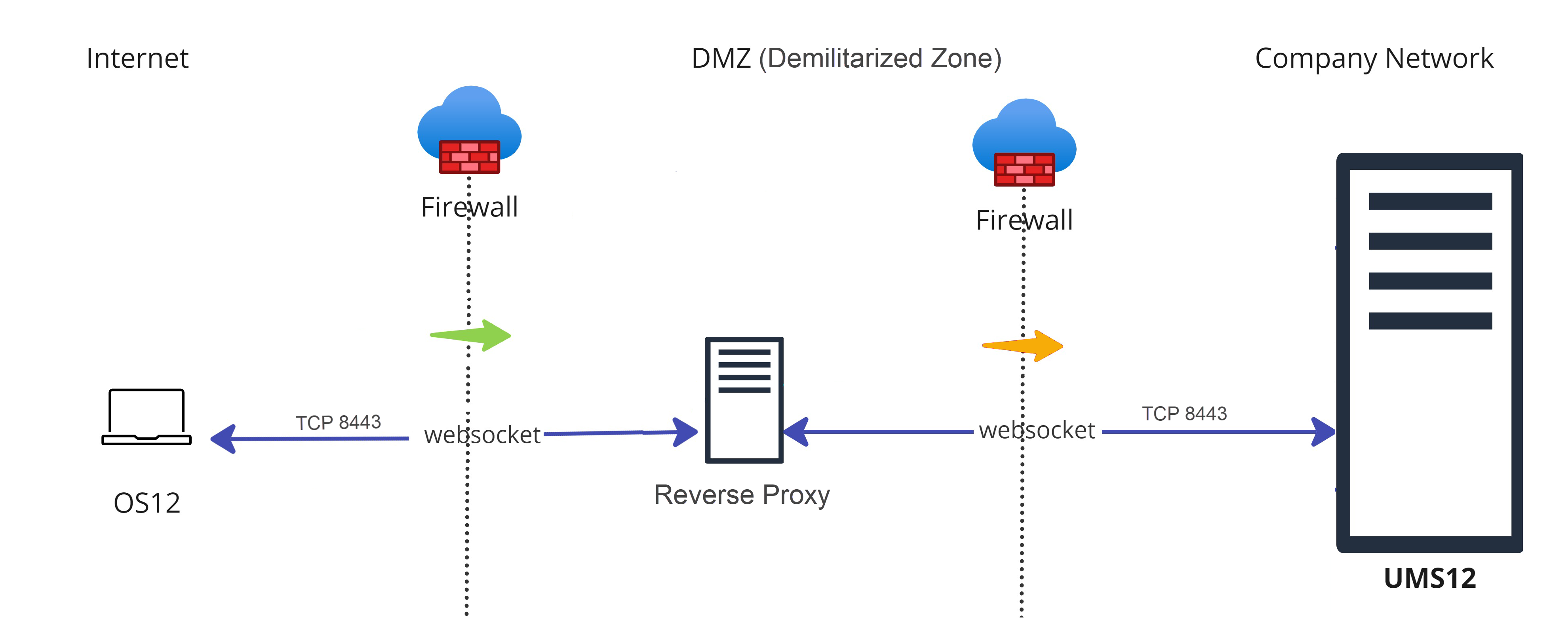
Legend to the image:
 : Shows that the traffic in the WebSocket runs in both directions.
: Shows that the traffic in the WebSocket runs in both directions. (multicolored): Shows from which side firewalls etc. must be opened.
(multicolored): Shows from which side firewalls etc. must be opened.
Technical Details
Reverse proxy with SSL offloading is possible as of UMS 12.02. See IGEL Cloud Gateway vs. Reverse Proxy for the Communication between UMS 12 and IGEL OS Devices .
The FQDN and port of the reverse proxy must be specified as a Cluster Address, see Server Network Settings in the IGEL UMS .
A reverse proxy / load balancer can also be used to distribute traffic from devices within the company network. For more information on network component integration, see IGEL Universal Management Suite Network Configuration.
It is advisable to use TLS 1.3 for the reverse proxy configuration.
Advantages
Load balancing
UMS as an Update Proxy feature can be used, i.e. IGEL OS devices can download the apps from the UMS Server. See Configuring Global Settings for the Update of IGEL OS Apps .
Adds an extra layer of security (depending on the configuration)
Disadvantages
Can be used if you manage IGEL OS 12 devices only.
Proper configuration and maintenance of the reverse proxy is required. For security reasons, you may want to restrict access to any components you do not require, but note that the following paths must be enabled:
For IGEL OS 12 device onboarding and communication: TCP 8443
/device-connector/*For IGEL OS 12 and UMS as an Update Proxy feature: TCP 8443
/ums-appproxy/*For the UMS Web App: TCP 8443
/wums-app/*and/webapp/*
If used to connect devices from outside the company network, the devices have an inbound connection to the UMS. In comparison, with the ICG, there is no inbound connection from the devices to the UMS.
If the reverse proxy gets compromised, it can provide access to the UMS. In comparison, if the ICG gets compromised, the UMS is NOT compromised at the same time.
Option 3: Direct Connection of the Devices to the UMS via Unified Protocol (No ICG, No Reverse Proxy)
In this case, IGEL OS 12 devices communicate directly with the UMS, see Devices Contacting UMS .
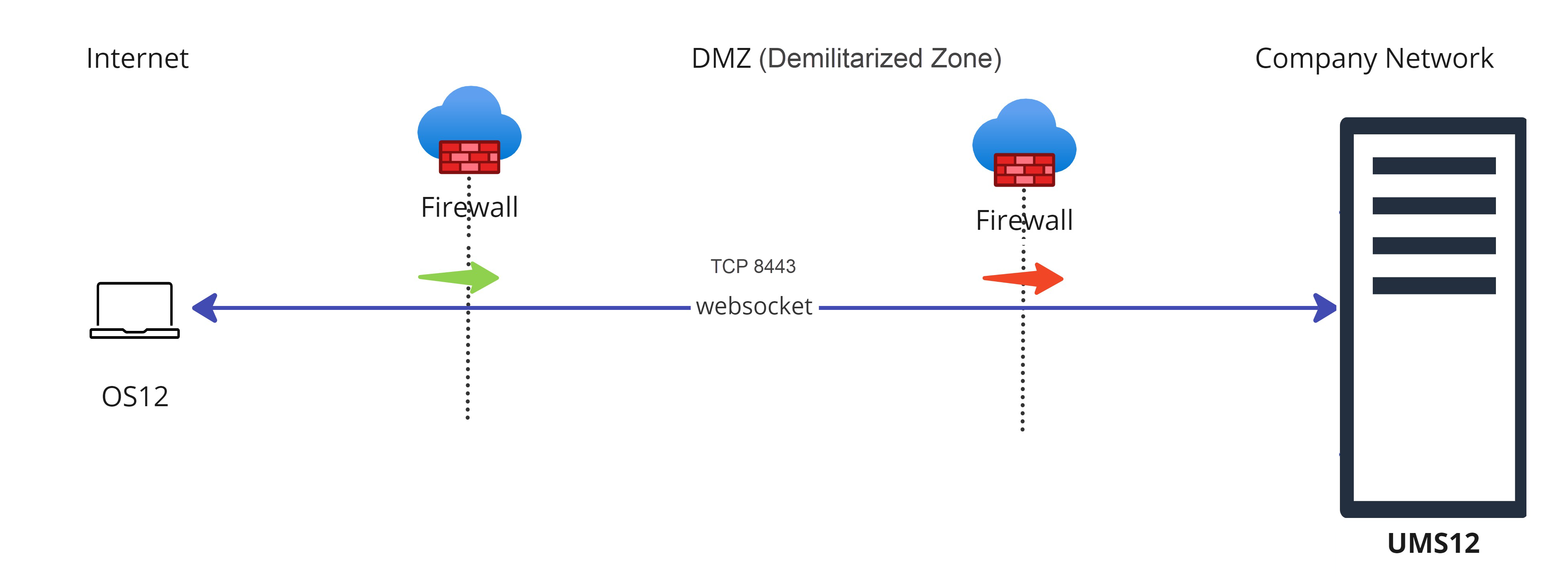
Legend to the image:
 : Shows that the traffic in the WebSocket runs in both directions.
: Shows that the traffic in the WebSocket runs in both directions. (multicolored): Shows from which side firewalls etc. must be opened.
(multicolored): Shows from which side firewalls etc. must be opened.
Advantages
port 8443 (can be changed under UMS Administrator > Settings > Web server port) must be opened in a firewall, but no other configuration is required
suitable for communication with devices within the company network
Disadvantages
Inbound connection from the device to the UMS
For communication with devices outside the company network, it is advised to consider the use of a reverse proxy or the ICG
IGEL Onboarding Service (OBS) is NOT a substitute for an ICG or a reverse proxy and is only meant to authenticate and register the endpoint device with the correct UMS during the onboarding. For more information on the OBS, see How to Start with IGEL > Initial Configuration of the IGEL Onboarding Service OBS and Onboarding IGEL OS 12 Devices.
