IGEL UMS and Devices: Secure Shadowing Communication Flow
This article describes the communication flow of a secure shadowing session in the IGEL Universal Management Suite (UMS) environment.
IGEL OS 12
Shadowing of IGEL OS 12 devices is always secure, i.e. via the Unified Protocol. The communication is always encrypted.
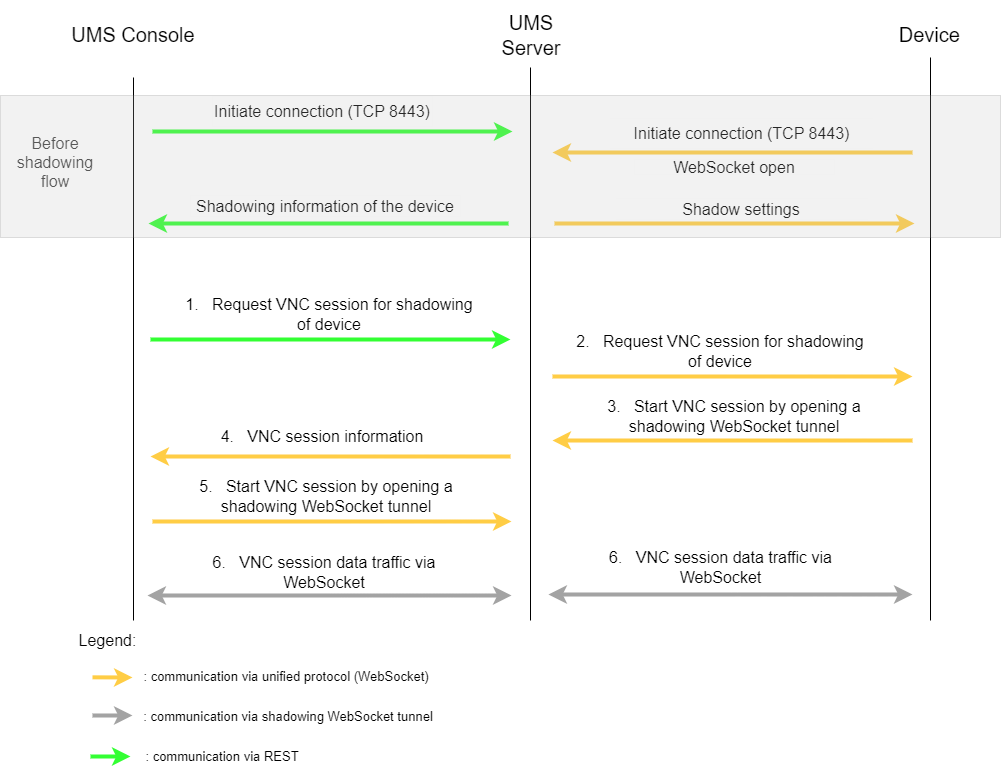
Direct Connection - UMS Console (Internal / External VNC Viewer)
Before the shadowing communication flow:
REST connection is initiated between the Console and the UMS Server
Unified Protocol WebSocket connection is initiated between the Device and the UMS Server
Shadow settings and information are forwarded
Shadowing flow:
The UMS Console requests the UMS Server to initiate a VNC session for shadowing.
The UMS Server requests the device to open a VNC session for shadowing.
The device opens the shadowing WebSocket tunnel to the UMS Server and starts the VNC session.
The UMS Server forwards the VNC session information to the UMS Console.
The UMS Console opens the shadowing WebSocket tunnel and starts the VNC session.
The VNC data is sent through the opened WebSocket tunnels between the UMS Console and the UMS Server and between the UMS Server and the Device.
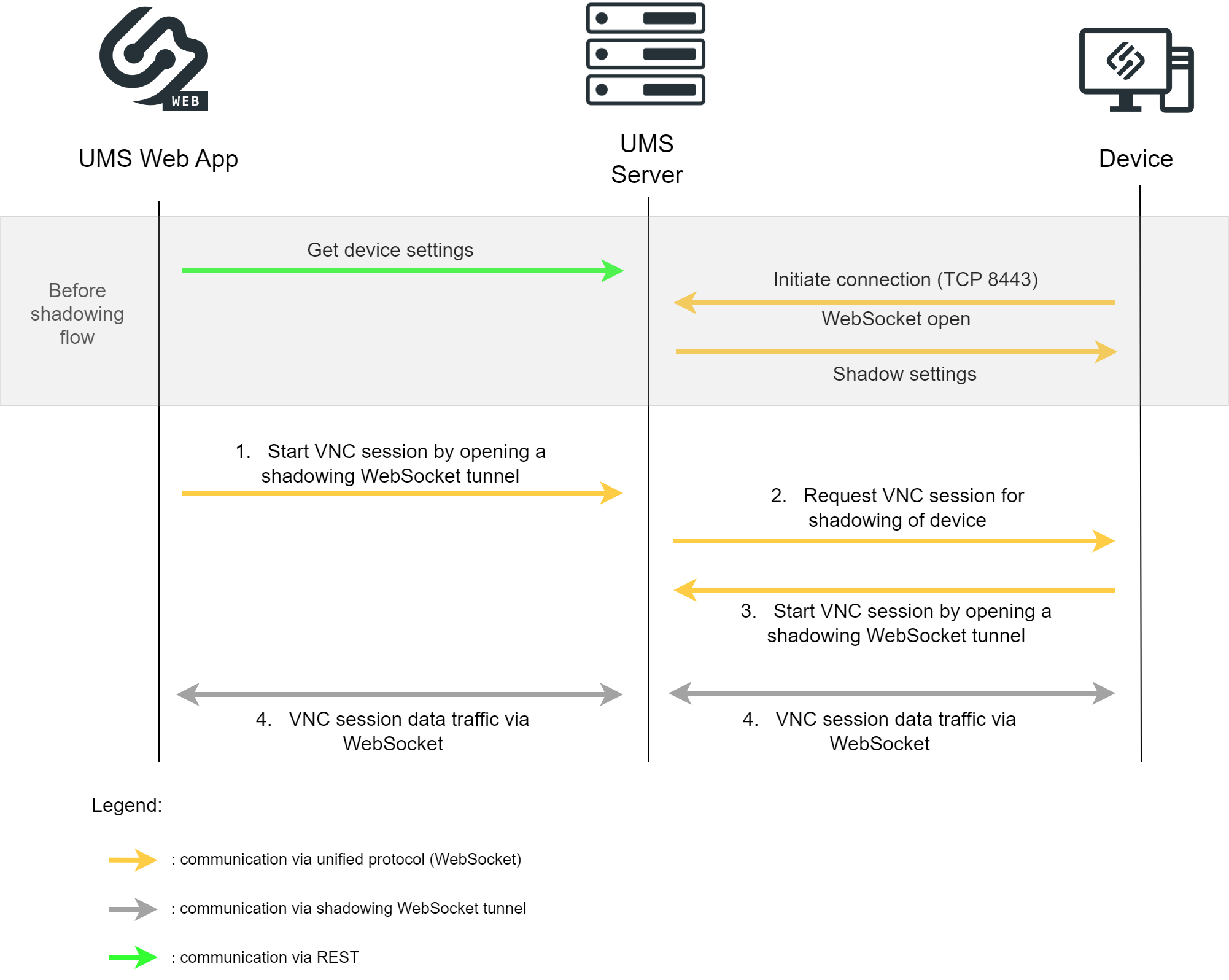
Direct Connection - UMS Web App
Before the shadowing communication flow:
Device settings are sent to the UMS Server through REST
Unified Protocol WebSocket connection is initiated between the Device and the UMS Server
Shadow settings are forwarded
Shadowing flow:
The UMS Web App starts the VNC session by opening the shadowing WebSocket tunnel to the UMS Server with information on the device to be shadowed.
The UMS Server requests the device via the Unified Protocol WebSocket to open a VNC session for shadowing.
The device opens the shadowing WebSocket tunnel to the UMS Server and starts the VNC session.
The VNC data is sent through the opened WebSocket tunnels.
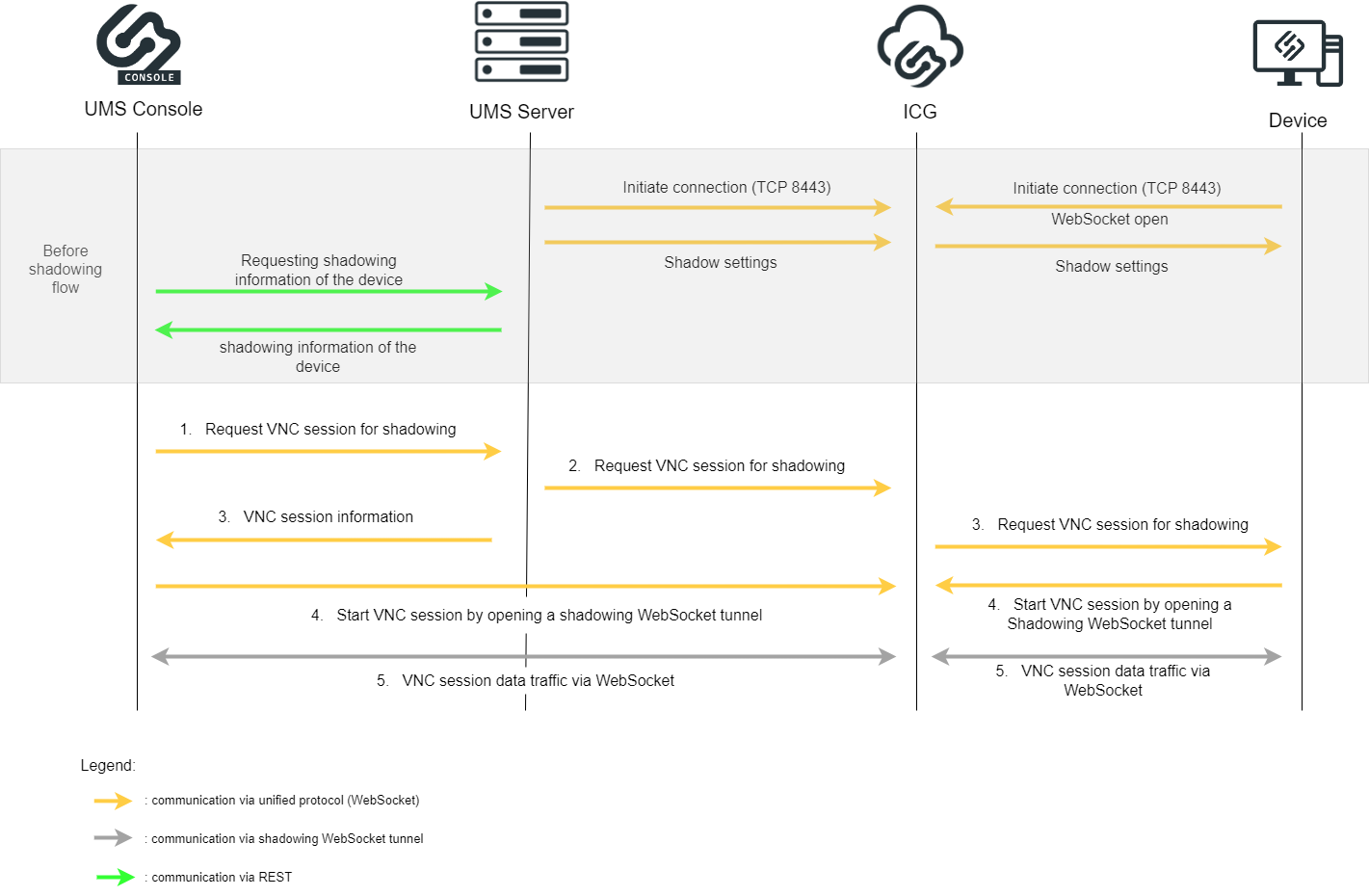
Over ICG - UMS Console (Internal / External VNC Viewer)
Before the shadowing communication flow:
Unified Protocol WebSocket connections are initiated between the UMS Server and the ICG and between the Device and the ICG
Shadow settings are forwarded
UMS Server sends shadowing information through REST to the UMS Console
Shadowing flow:
The UMS Console requests the UMS Server to initiate a VNC session for shadowing.
The UMS Server requests the ICG to open a VNC session for shadowing.
The UMS Server sends the VNC information to the UMS Console and the ICG requests the device to open a VNC session for shadowing.
The device opens the shadowing WebSocket tunnel to the ICG and starts the VNC session and the UMS Console opens the shadowing WebSocket tunnel to the ICG and starts the VNC session.
The VNC data is sent through the opened WebSocket tunnels.
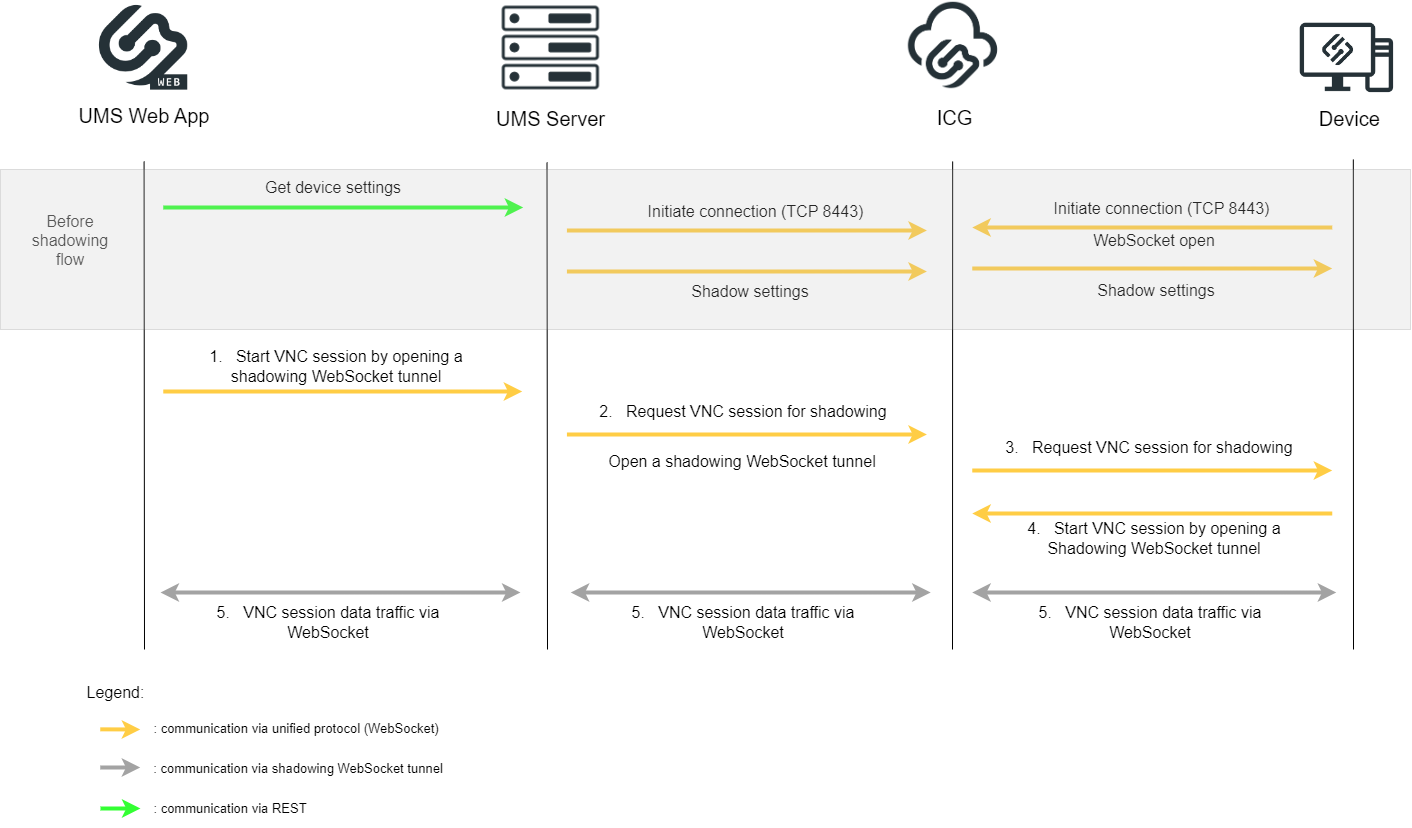
Over ICG - UMS Web App
Before the shadowing communication flow:
Device settings are sent to the UMS Server through REST
Unified Protocol WebSocket connections are initiated between the UMS Server and the ICG and between the Device and the ICG
Shadow settings are forwarded
Shadowing flow:
The UMS Web App starts the VNC session by opening the shadowing WebSocket tunnel to the UMS Server with information on the device to be shadowed.
The UMS Server requests the ICG to open a VNC session for shadowing and opens a WebSocket tunnel for the shadowing.
The ICG requests the device to open a VNC session for shadowing.
The device opens the Shadowing WebSocket to the ICG and starts the VNC session.
The VNC data is sent through these WebSockets.
IGEL OS 11 or Earlier
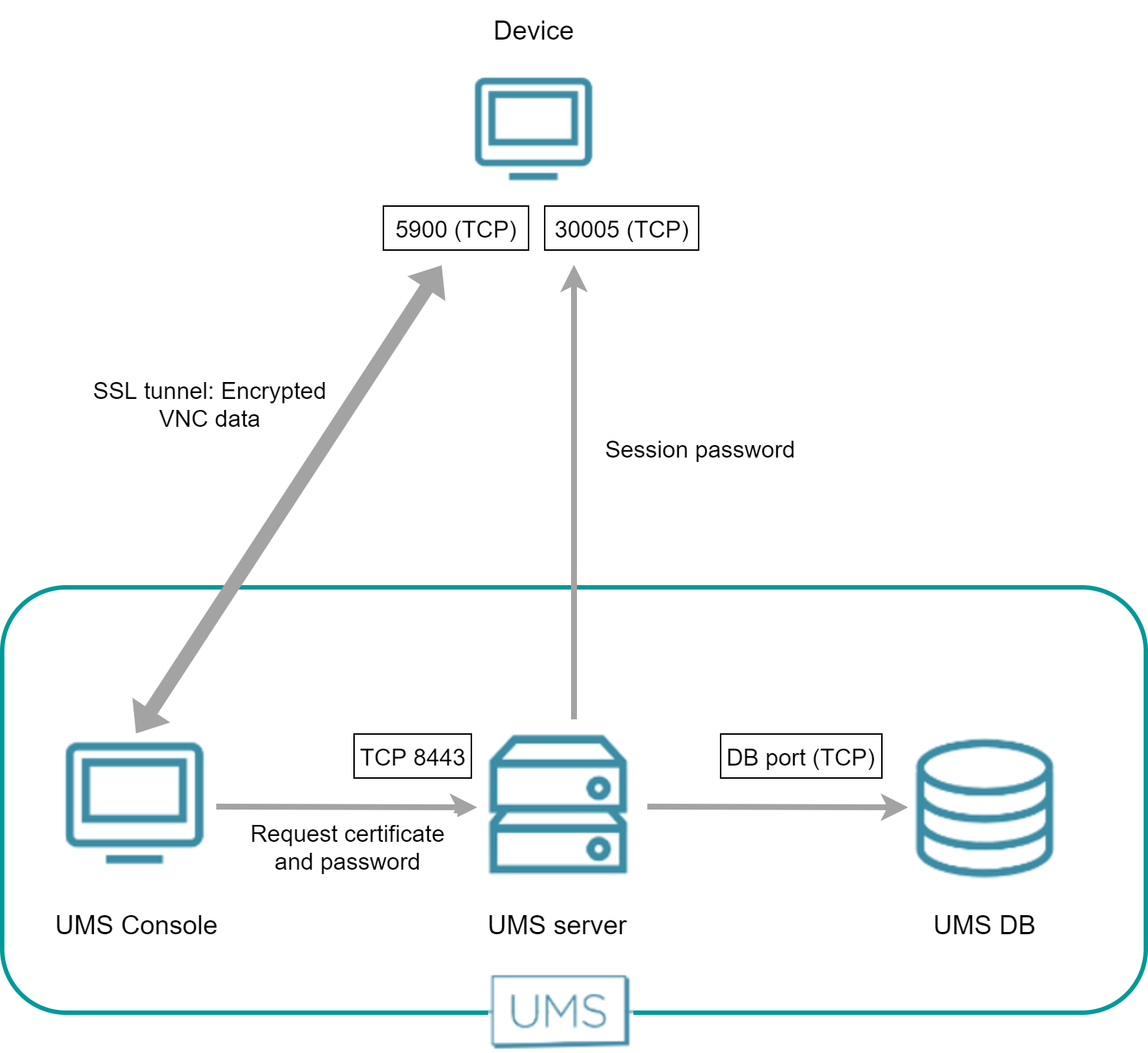
Direct Connection - Internal VNC Viewer
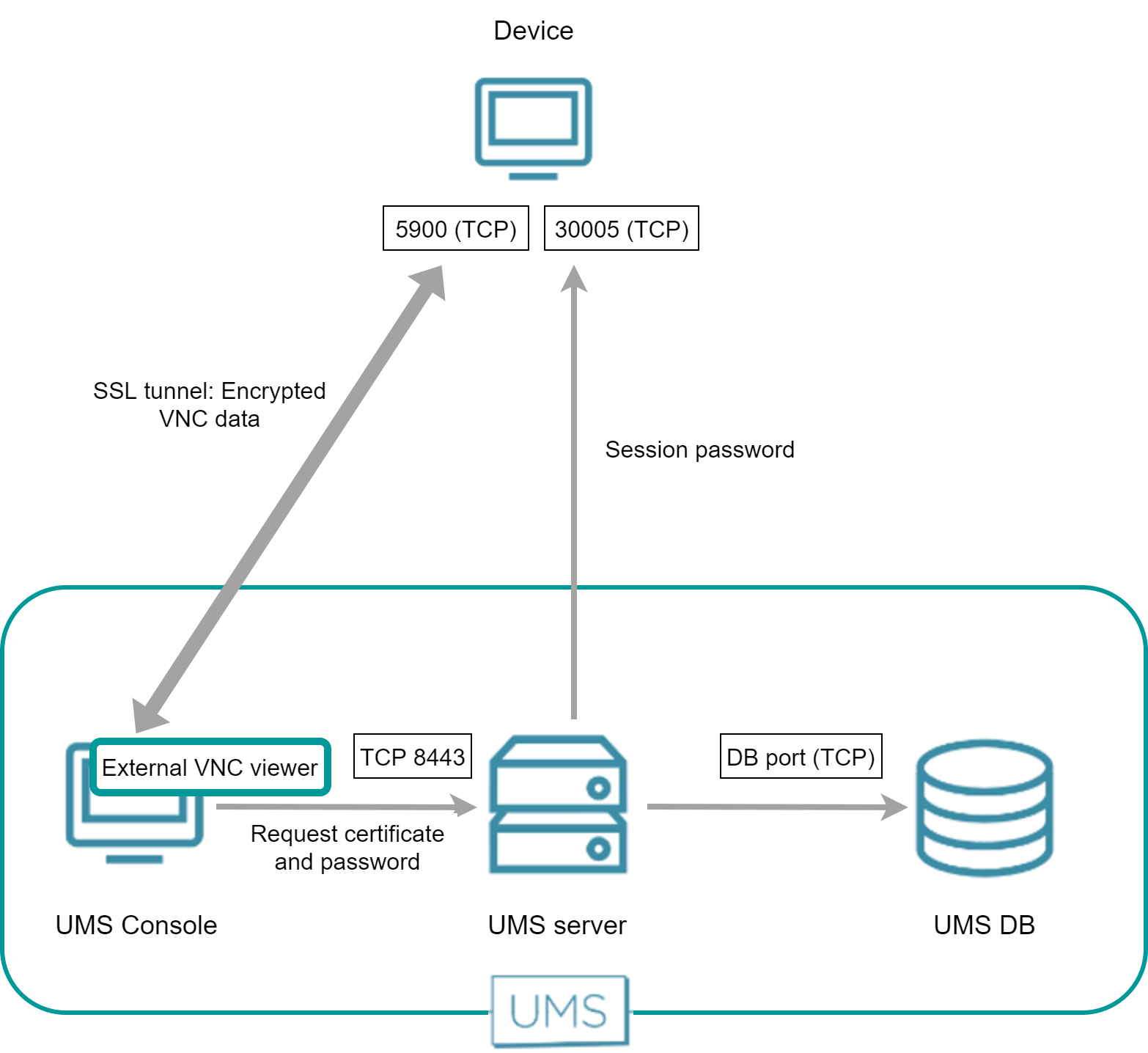
The UMS Console requests the device's certificate and the session password from the UMS Server. The UMS Console then establishes an SSL tunnel with the device using the session password. The device sends the certificate to the UMS Console; the UMS Console checks the certificate against the certificate it has received from the UMS Server. In return, the UMS Console sends the session password to the device. After that, the SSL tunnel between the UMS Console and device is established and can be used for exchanging VNC data.
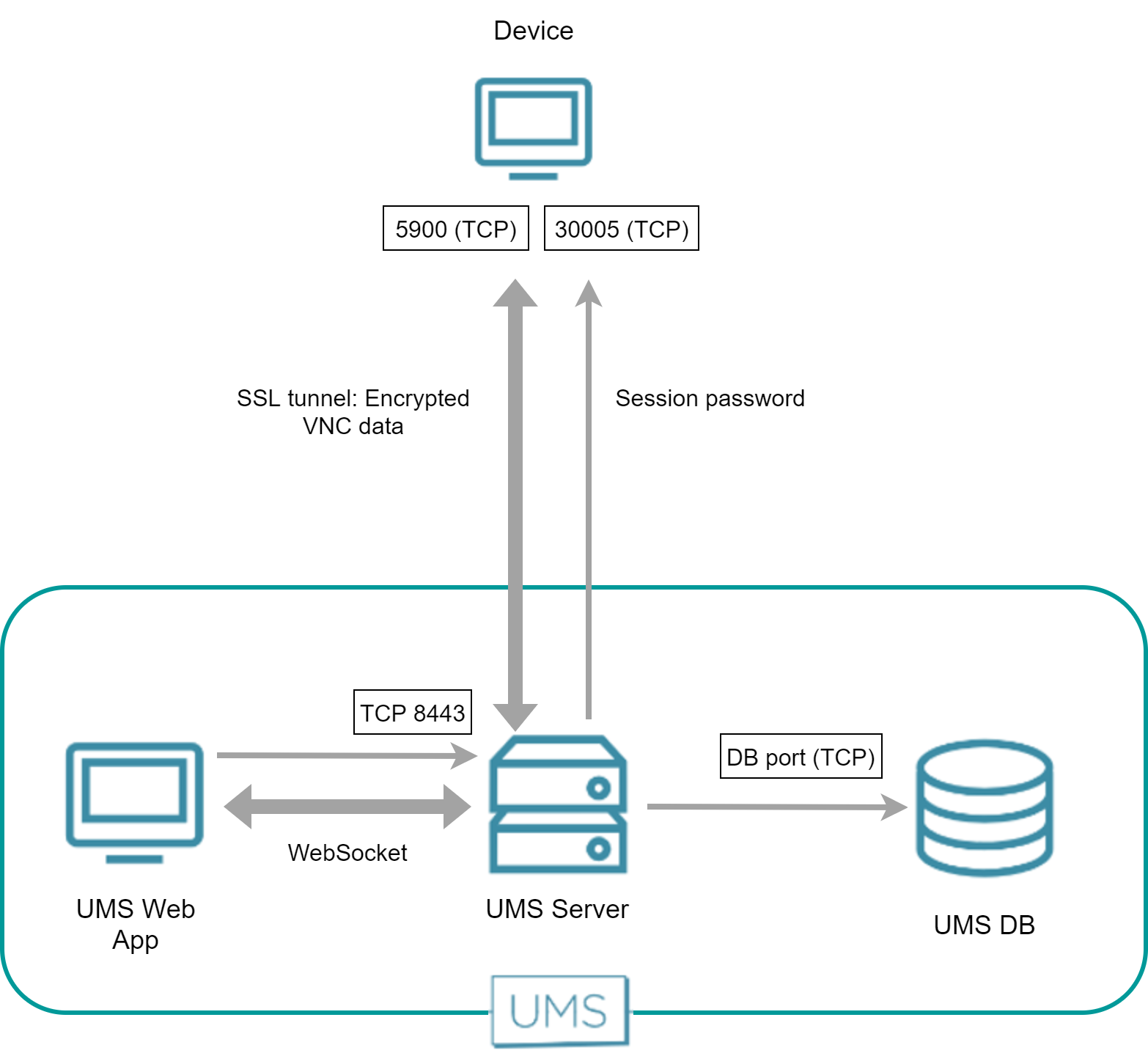
Direct Connection - UMS Web App
The UMS Web App requests the UMS Server to initiate a VNC session for shadowing. The UMS Server establishes an SSL tunnel with the device using a session password and the device's certificate. The UMS Web App and the UMS Server communicate via WebSocket, which also carries the VNC data.
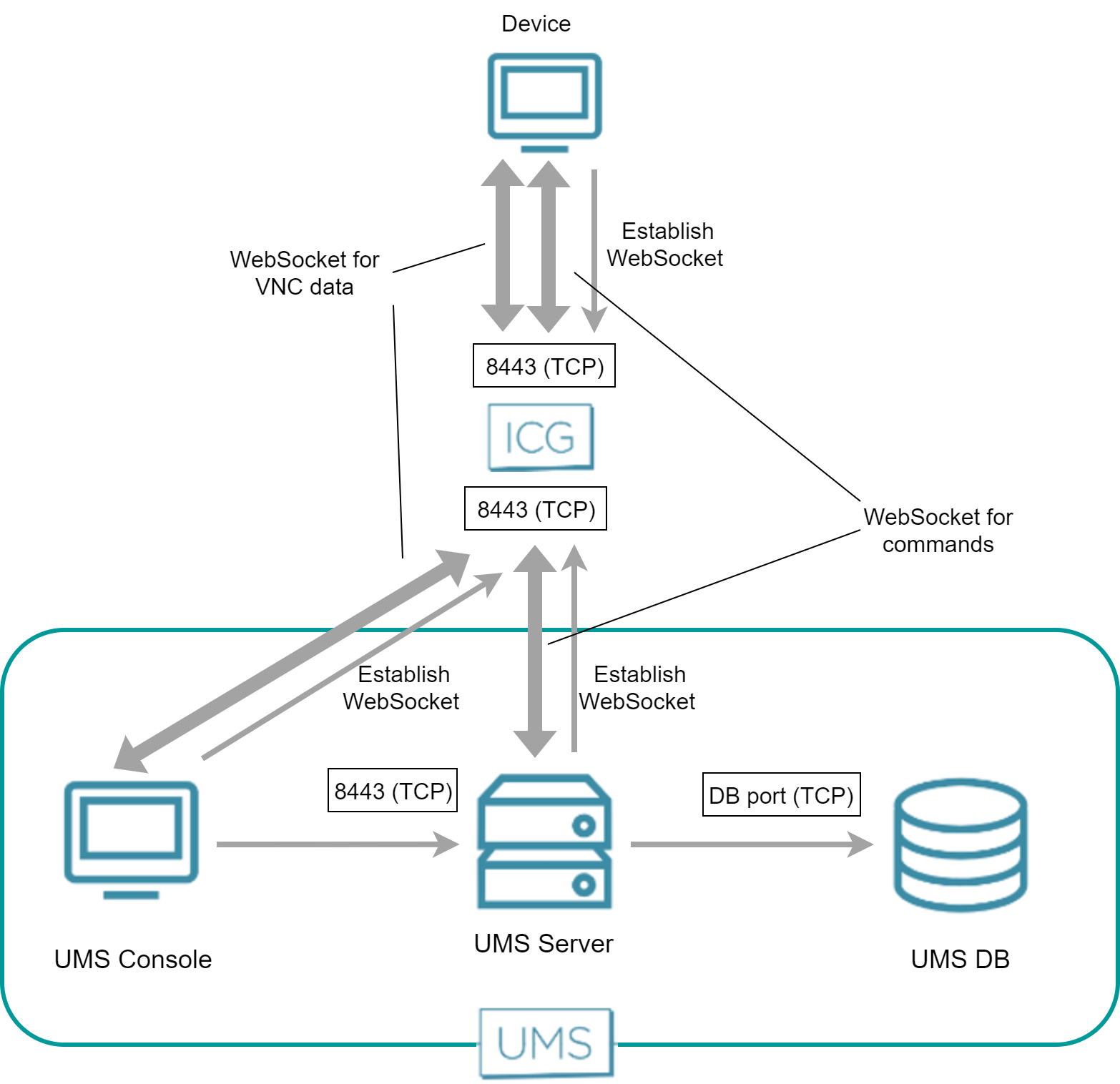
Over ICG - Internal VNC Viewer
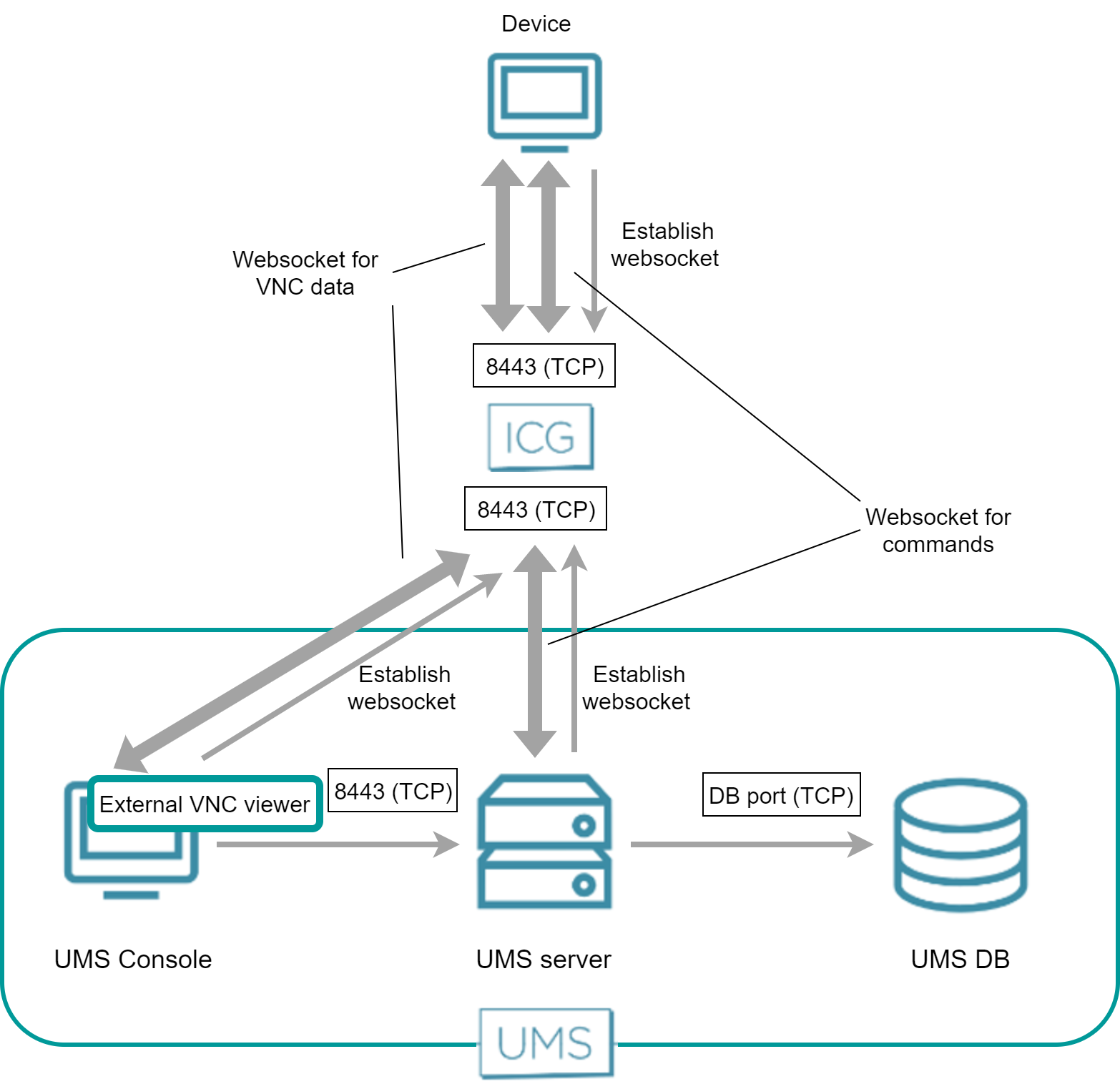
Both the UMS Server and the device have established a WebSocket connection to the ICG; this WebSocket is used for commands from the UMS and messages from the device.
The UMS Console and the device establish a dedicated WebSocket for secure shadowing with the ICG.
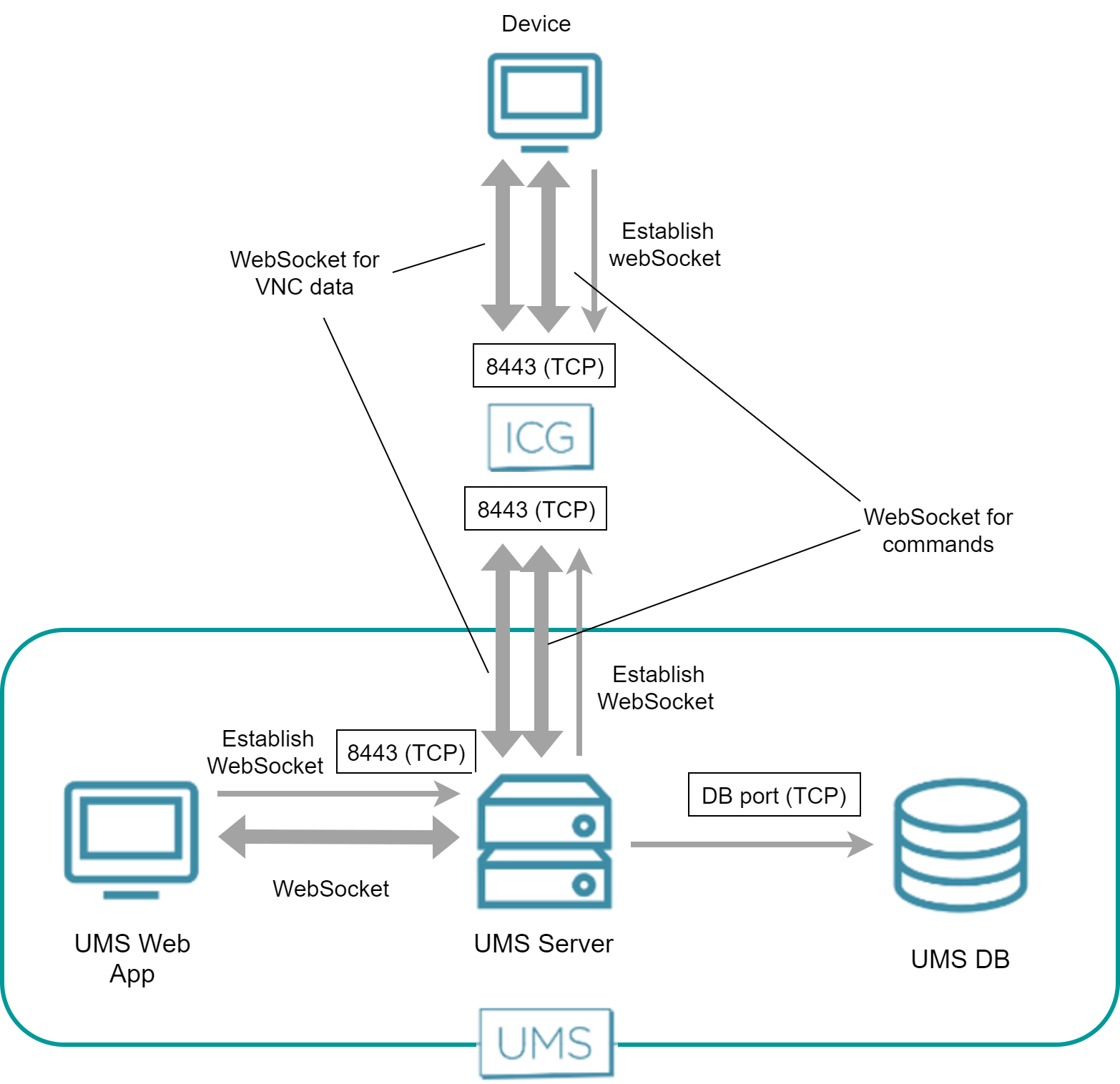
Over ICG - UMS Web App
The UMS Web App requests the UMS Server to initiate a VNC session for shadowing. The UMS Server creates an additional WebSocket connection for exchanging the VNC data. The UMS Web App and the UMS Server communicate via WebSocket, which also carries the VNC data.
Direct Connection - External VNC Viewer
The external VNC viewer runs on the same machine as the UMS Console. The UMS Console starts the external viewer and then acts as a proxy between the device and the external VNC viewer.
Over ICG - External VNC Viewer
The external VNC viewer runs on the same machine as the UMS Console. The UMS Console starts the external viewer and then acts as a proxy between the ICG and the external VNC viewer.