IGEL UMS Administrator Command-Line Interface
The Universal Management Suite (UMS) Administrator command-line interface (CLI) allows you to control the IGEL UMS Administrator via a terminal and to automate UMS Administrator actions via scripting. Among these actions are creating and editing database connections for the UMS Server, backing up and restoring the embedded database, configuring communication ports and security, managing the UMS ID, configuring the superuser, and restarting the UMS Server.
As this feature allows complete control without any graphical desktop environment, it is possible to run the CLI application on headless Linux systems.
Basic Usage
Like the graphical UMS Administrator application, the CLI requires elevated privileges.
→ Windows: Open a command prompt (cmd.exe) as Administrator.
→ Linux: Become root or use sudo
You can run the main command umsadmin-cli from any directory, as the command is made available on the PATH.
→ To see the global options and the primary subcommands, enter umsadmin-cli
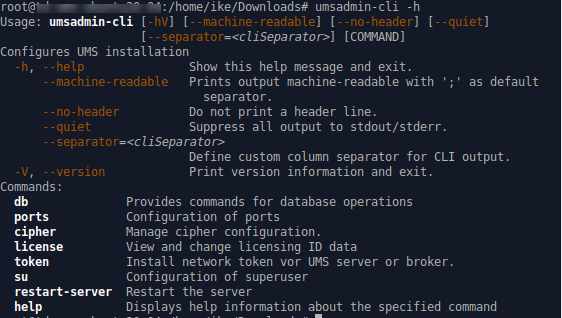
→ To get all possible options for a specific subcommand, enter umsadmin-cli followed by the subcommand, e.g. umsadmin-cli db create
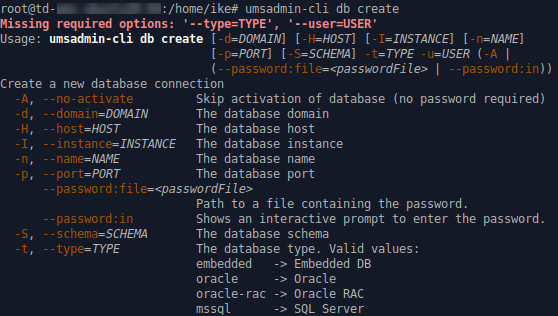
Certain subcommands have no options and run immediately. Please refer to the Command Reference.
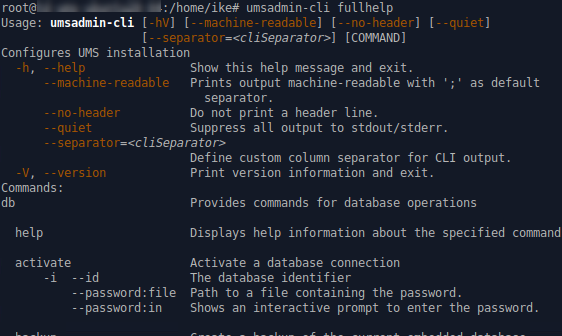
→ To get the complete online help with all commands, enter umsadmin-cli fullhelp
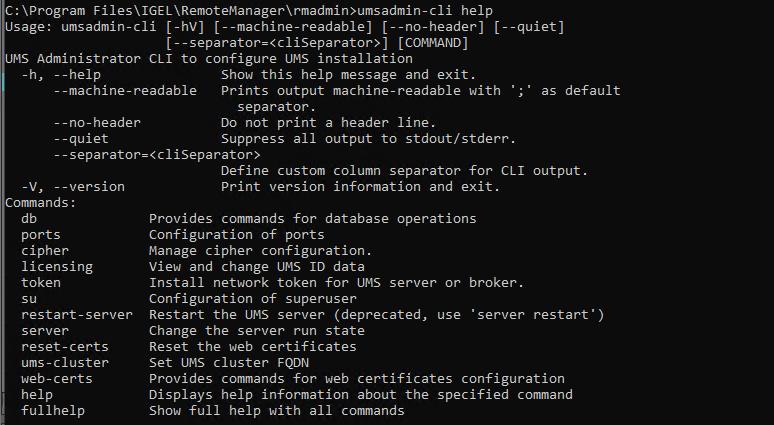
→ To get the list of available commands, enter umsadmin-cli help
→ To display help information about any command, use help as a subcommand. For example, enter umsadmin-cli web-certs help
Global Options
If you intend to use the UMS Administrator CLI in a script, you may want to configure its output to stdout/stderr according to your needs. This makes it easy to further process the output of umsadmin-cli and extract any relevant data.
Please see the available options below.
--machine-readable
Prints output machine-readable with a semi-colon (;) as default separator.
Example:
root@machine:/home/locadmin# umsadmin-cli --machine-readable db list ACTIVE;DATABASE;HOST;USER;DB-TYPE;ID true;rmdb;localhost;root;Embedded DB;1
--no-header
No header line is printed. (Not all commands print a header.)
Example:
root@machine:/home/locadmin# umsadmin-cli --machine-readable --no-header db list true;rmdb;localhost;root;Embedded DB;1
--quiet
All output to stdout/stderr is suppressed for some commands which might take a long time to execute. These are, for instance, db backup, db restore, db copy, and server-restart.
Example:
root@machine:/home/locadmin# umsadmin-cli --quiet db backup -o /tmp/mybackup02.pbak --fullroot@machine:/home/locadmin#
It is still possible to redirect all output to a null device using operating system functions. For example, to redirect standard output and error output to the null device on Linux, use:
command … >/dev/null 2>&1
--separator
Defines a custom column separator for output to stdout/stderr.
Example:
root@machine:/home/locadmin# umsadmin-cli --machine-readable --no-header --separator "||" db list true||rmdb||localhost||root||Embedded DB||1
Some separator characters, such as the pipe symbol (|), require quotes because they have special functions in terminals.
Exit Codes
Exit Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
0 | Successful execution |
1 | Internal error. An error number is outputted to stderr; for details, see Error Numbers. |
2 | Wrong usage of the CLI or invalid arguments |
Command Reference
General Usage of Password Options
Some commands require a password. Entering the password in plain text on the command line is not secure and therefore not possible. Therefore, one of the following password options must be used:
--password:in for interactively entering the password (possibly with confirmation)
--password:file <FILE> for providing a file containing the password
A password file must have the password as the first line and the passwords must not be pure whitespace. Additional lines with content are allowed but will not be evaluated.
UMS Server Restart Required
Most of the commands in the sections "Ports", "Cipher", "Reset Certificates", and "Superuser" change the UMS configuration and a restart of the UMS server is required to make the new settings take effect. This can be done in two ways:
Use the appropriate function of the OS (e.g.
systemctlon Linux)Use the command
umsadmin-cli server restart
Database
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Value Type | Option Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
List all configured data sources |
|
| Shows the ID of the data source, which is required by other commands. The lowest ID is 1. IDs may change upon the creation and deletion of data sources. It is strongly recommended to always extract the ID before using it in other commands with --id The ID is calculated like this: highest existing ID + 1 | ||||
Show all details of a database |
|
|
|
| integer | The ID of the database to show | Run Run |
Create a new database connection |
|
|
|
| string | The database type. | Type, user, and port are required. Other options may or may not be required depending on the DB type
If activation fails, the data source entry will still be present and is not active (same behavior as in the graphical UMS Administrator). 'rmdb' is a reserved name for the embedded database type and cannot be used for other types. |
|
| string | The database host | ||||
|
| string | The database domain | ||||
|
| integer | The database port | ||||
|
| string | The database username | ||||
|
| string | The database schema | ||||
|
| string | The database name. Free text, except 'rmdb'; this name is reserved for the embedded database. | ||||
|
| string | The name of the database instance | ||||
|
| The database will not be activated. | |||||
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. | |||||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. | |||||
Edit a data source |
|
|
|
| string | The database type. | Embedded databases cannot be edited (as in the graphical UMS Administrator). All options are optional, except |
|
| string | The database host | ||||
|
| string | The database domain | ||||
|
| integer | The identifier of the database to be edited | ||||
|
| string | The name of the database instance | ||||
| string | Additional JDBC parameter. | For details on the JDBC parameters, see How to Set Up a Data Source in the IGEL UMS Administrator. Examples:
| ||||
|
| string | The database name. Free text, except 'rmdb'; this name is reserved for the embedded database. | ||||
|
| integer | The database port | ||||
|
| string | The database schema | ||||
|
| string | The database username | ||||
Activate a database connection |
|
|
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. Example: | ||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. | |||||
|
| integer | The identifier of the database to be activated | ||||
Deactivate the active database connection |
|
|
|
| integer | The identifier of the database to be deactivated | |
Test the active database connection |
|
|
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. Example: | ||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. | |||||
Optimize the active database |
|
| This command can only be applied to an embedded database or a Derby database. | ||||
Create a copy of the current database |
|
|
|
| integer | The ID of the target database To get the database ID, enter | |
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. | |||||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. | |||||
Delete a database connection |
|
|
|
| integer | The ID of the database connection that is to be deleted | |
Create a backup of the current embedded database |
|
|
|
| Path to the target file. The file suffix Existing backup files are not overwritten. | ||
|
| Full backup. Database, server configurations, and transfer files are included. | |||||
|
| All directories for the specified path will be created if they are not already existing. | |||||
Restore a backup into the embedded database |
|
|
|
| Path to the backup file |
Ports
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Value | Option Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
List all ports and SSL flag |
|
| ||||
Set new port numbers or SSL-only flag |
|
|
|
| integer | Device communication port. For details, see Devices Contacting UMS. |
|
| integer | Java Web Start port | |||
|
| integer | UMS server port. For details, see UMS with Internal Database and UMS with External Database. | |||
|
| integer | Embedded database port | |||
| boolean | Allow SSL connections only |
Cipher
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Option Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
List all ciphers, optionally filtered |
|
| List all ciphers | ||
|
| List only enabled ciphers | |||
|
| List only disabled ciphers | |||
Enable ciphers |
|
| Enable ciphers. The ciphers are separated by whitespaces. Example: | ||
| Apply for all; individual cipher names are ignored. | ||||
Disable ciphers |
|
| Disable ciphers. The ciphers are separated by whitespaces. Example: | ||
| Apply for all; individual cipher names are ignored. |
Manage Web Certificates
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Option Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Reset web certificates |
|
|
| The reset is only executed after confirmation | ||
Assign certificate to current or all servers |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | |
|
| Server to which the certificate is assigned. Possible values:
| ||||
Create a root certificate |
|
|
|
| Key pair algorithm; | |
|
| Country code (two letters) | ||||
|
| Expiration date (YYYY-MM-DD) (Current date plus 20 years if not specified.) | ||||
| Key size (4096, 8192, ... bits). Valid values :
| |||||
|
| Locality (If not specified, the hash code of a random uuid is used.) | ||||
|
| Certificate name | ||||
| Named curve.
| |||||
|
| Organization (Mandatory option) | ||||
Create signed certificate |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of parent CA certificate | The parent CA certificate is specified by the SHA1 fingerprint. It doesn’t matter whether you use no delimiter, ‘-’ or ‘:’ as the delimiter for the fingerprint. |
|
| Certificate name | ||||
| Common name | |||||
|
| Country code (two letters) | ||||
|
| Organization | ||||
|
| Locality (If not specified, the hash code of a random uuid is used.) | ||||
|
| Expiration date (YYYY-MM-DD) (Current date plus 1 year if not specified.) | ||||
| Certificate type:
| |||||
|
| Hostname (hostname or one of these values:
| You can specify a list of hostnames for the subject alternative names (SAN) or you can specify, whether the current server (CURRENT_SERVER) or all servers (ALL_SERVER) should be listed in the SAN list. | |||
Delete a certificate |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | |
Export certificate |
|
|
|
| Path to which the certificate should be exported | |
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | ||||
Export certificate chain to keystore (JKS) |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | |
|
| Path to keystore to which certificate chain should be exported | ||||
| Path to a file containing the password | |||||
| Shows an interactive prompt to enter the password | |||||
Import certificate chain from keystore |
|
|
|
| The keystore file | |
| Path to a file containing the password | |||||
| Shows an interactive prompt to enter the password | |||||
Import decrypted private key |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of parent CA certificate | |
|
| The file containing the private key | ||||
Import root certificate |
|
|
|
| The root certificate | |
Import signed certificate |
|
|
|
| The root certificate ( | A certificate can only be imported when no other certificate with the same fingerprint already exists; otherwise, you will get an error message. |
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of parent CA certificate | ||||
List the assigned server of a certificate |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | |
List all web certificates or details of a certificate |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | When you specify a fingerprint, the details of the certificate with that fingerprint are shown. |
Renew certificate |
|
|
|
| SHA1 fingerprint of certificate | You only have to specify the fingerprint of the certificate that should be renewed. If the other parameters are not specified, the values from the old certificate are used (with a new expiration date). |
|
| Certificate name | ||||
| Common name | |||||
|
| Country code (two letters) | ||||
|
| Organization | ||||
|
| Locality | ||||
|
| Expiration date (YYYY-MM-DD) | ||||
|
| Hostname (hostname or one of these values:
|
Superuser
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Value | Option Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Show UMS superuser |
|
| ||||
Change UMS superuser |
|
|
|
| string | New superuser |
|
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. | |||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. |
UMS ID
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Value | Option Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Show the current UMS IDs |
|
| ||||
Create a new UMS ID |
|
| ||||
Backup the UMS ID |
|
|
|
| string | Path to the target file (file suffix: |
|
| All directories for the specified path will be created if they are not already existing. | ||||
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. | ||||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. | ||||
Restore a UMS ID from a backup |
|
|
|
| string | Path to the backup file |
| string | The password is read from a file (plain text) whose path is provided after this option. | ||||
| string | The password is read from stdin; an interactive prompt is shown. |
Network Token
Action | Primary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Value | Option Description | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Install a network token for the UMS Server or a broker (UMS HA) |
|
|
| string | Path to token file | This command is also available as a standalone command named |
| boolean | Install token for UMS Server | ||||
| boolean | Install token for broker |
UMS Cluster
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Option Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Show the current UMS cluster FQDN |
|
| |||
Set a new UMS cluster FQDN |
|
|
|
| Name for the new UMS cluster FQDN |
Delete the current UMS cluster FQDN |
|
|
Server
Action | Primary Subcommand | Secondary Subcommand | Short Option | Long Option | Option Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Start the local UMS Server |
|
| |||
Stop the local UMS Server |
|
| |||
Restart the local UMS Server |
|
| |||
End the update mode of the local UMS Server |
|
| |||
Set the distributed mode of the UMS installation |
|
|
|
| Enable Distributed UMS |
|
| Disable Distributed UMS | |||
Error Numbers
The error numbers are printed in the following format:
<E-NNNN>: <HUMAN READABLE MESSAGE>
Some error descriptions in the following table contain the phrase „[param]“. These will be replaced during runtime with details for the relevant error, e.g. the problematic path for E-1030.
Error number | Error description |
|---|---|
1000 | Unable to connect to database. UMS server may be down. |
1001 | Cannot get database configurations. |
1002 | Cannot create database. |
1003 | Cannot activate database. [param] |
1004 | Internal error while activating database. |
1005 | Database already exists in this configuration. |
1006 | Database type is unknown. |
1007 | Database is already activated. |
1008 | Cannot edit database configurations. |
1009 | Internal error while optimizing database. |
1010 | The active data source type is not Embedded or Derby and does not support optimization. |
1011 | Test of the active data source failed. |
1012 | No database is activated. |
1013 | Cannot deactivate database. |
1014 | No database is active or the active database is not of type 'Embedded' or 'Derby'. |
1020 | Database could not be deleted. |
1030 | The specified directory for the backup does not exist: [param] |
1031 | Internal error while attempting database backup. |
1040 | The specified backup file was not found. |
1041 | The specified backup file has an invalid file type. |
1042 | Unable to read the specified backup file. |
1043 | Internal error while activating data source after restore. |
1044 | Internal error while attempting to restore database. |
1045 | The active data source is not embedded or there is no active data source. |
1051 | Authentication error or internal error when an attempt was made to copy the database |
1052 | Error Accessing credentials of source database |
1090 | A name is required for non-embedded database types. |
1091 | Activation failed, incorrect password provided. |
1092 | Backup failed, the specified file already exists. |
1093 | Port number is required for non-Embedded database. |
1094 | A data source of the Embedded type cannot be edited. |
1095 | No such data source with this ID. |
1100 | The name 'rmdb' is reserved for the Embedded database. |
2000 | Internal error while reading port configuration. |
2001 | Internal error while setting port configuration. |
2002 | Internal error while restarting UMS server. |
2003 | Invalid port number provided. |
2004 | Port number [param] already configured. |
3000 | Internal error while reading cipher data. |
3001 | Internal error while changing cipher configuration. |
3002 | Invalid ciphers provided: [param] |
4000 | Resetting web certificates requires '--yes' option for confirmation. |
4001 | Internal error while resetting web certificates. |
5000 | Internal error while reading superuser credentials. |
5001 | Internal error while writing superuser credentials. |
5002 | No username was provided for new credentials. |
5003 | Unable to set superuser credentials. There is no active data source. |
6000 | Unable to create a new UMS ID. |
6001 | The specified file for the license key backup already exists. |
6002 | No internal license keystore found. |
6003 | Internal error while creating license key backup. |
6004 | Internal error while restoring license key backup. |
6005 | The specified file for the license key backup does not exist. |
6006 | The specified password for the license key backup is incorrect. |
6007 | The specified path for the license key backup does not exist: [param] |
7000 | Token file was not found. |
7001 | Setup type not defined, token not installed. |
7501 | Unable to set UMS cluster FQDN. |
7502 | Unable to show UMS cluster FQDN. |
7503 | Unable to delete the cluster FQDN. |
8000 | Internal error while restarting the UMS server. |
8001 | Internal error while starting the UMS server. |
8002 | Internal error while stopping the UMS server. |
8003 | Internal error while ending the update mode of the UMS Server. |
8004 | Internal error while setting the distributed mode of the UMS installation. |
8005 | Either --enable or --disable must be provided in the options. |
8006 | Distributed UMS not recommended for Derby Embedded Database. |
9000 | An error with the password file occurred: [param] |
9001 | The provided passwords did not match. Aborted. |
9002 | The provided password exceeds the maximum character limit ([param]) or contains only whitespace. |
9700 | File [param] doesn't exist! |
9701 | Keystore contains no certificate entries! |
9702 | Keystore password is invalid! |
9703 | Keystore couldn't be read! |
9704 | Could not import certificate chain! |
9705 | Internal error while importing certificate chain! |
9706 | No SHA1 fingerprint specified! |
9707 | Could not delete certificate(s) with SHA1 fingerprint [param]! |
9708 | Certificate must not be deleted because it is currently in use! |
9709 | Root certificate creation failed! |
9710 | Certificate could not be created! Private key of CA certificate is not known. |
9711 | Certificate could not be created! CA certificate is not valid. |
9712 | Could not find CA certificate with specified fingerprint. |
9713 | Certificate could not be created! CA certificate does not meet the requirements. |
9714 | Certificate could not be created! Requirements for CA certificate creation are not met. |
9715 | Creation of signed certificate failed! |
9716 | Certificate could not be created! Certificate name too long (only 200 characters are allowed)! |
9717 | Could not find certificate with specified fingerprint! |
9718 | Certificate could not be renewed! Certificate has no CA parent. |
9719 | Certificate file [param] doesn't exist! |
9720 | Certificate is invalid! |
9721 | Import of certificate failed! No CA certificate. |
9722 | Import of certificate failed! |
9723 | Import of certificate failed! Certificate is not valid. |
9724 | Import failed! Certificate doesn't contain any subject alternative names. |
9725 | Import of private key failed! File [param] doesn't exist. |
9726 | Import of private key failed! Private key is encrypted. Decrypt it before importing it. |
9727 | Import of private key failed! |
9728 | Certificate already has private key! |
9729 | Import of private key failed! Private key does not match the specified certificate. |
9730 | Export of certificate failed! Directory [param] doesn't exist. |
9731 | Export of certificate failed! |
9732 | Export of certificate chain failed! Directory [param] doesn't exist. |
9733 | Certificate must not be a root or CA certificate! |
9734 | Export of certificate chain failed! |
9735 | Password must be at least 6 characters long! |
9736 | Assignment of certificate failed! |
9737 | Private key is not known! |
9738 | Could not read certificate info! |
9739 | Import failed! Certificate with same fingerprint already exists. |
9740 | Import failed! No valid root certificate. |
9741 | Import failed! Verification of signature failed. |
9742 | Import failed! No valid CA certificate available. |
9743 | Could not read assigned server info! |
9744 | Could not find certificate with specified fingerprint or no server is assigned to certificate! |
9745 | Common name is invalid! Only A-Z, a-z, 0-9, - and . are allowed. |
