Download PDF
Download page Wi-Fi Networks.
Wi-Fi Networks
This article shows how to configure wireless network connections in IGEL OS. All the wireless network connections configured for the device are shown in the list, including connections configured through the UMS or the Wi-Fi tray app. For more information on the tray app, see Wi-Fi Tray App.
Menu path: Network > Wireless > Wi-Fi Networks
To edit the Wi-Fi networks list, proceed as follows:
- Click
 to create a new entry.
to create a new entry. - Click
 to remove the selected entry.
to remove the selected entry. - Click
 to edit the selected entry.
to edit the selected entry. - Click
 to copy the selected entry.
to copy the selected entry.
Clicking
![]() brings up the Add dialogue, where you can define the settings of the wireless network.
brings up the Add dialogue, where you can define the settings of the wireless network.
Wi-Fi Networks Settings
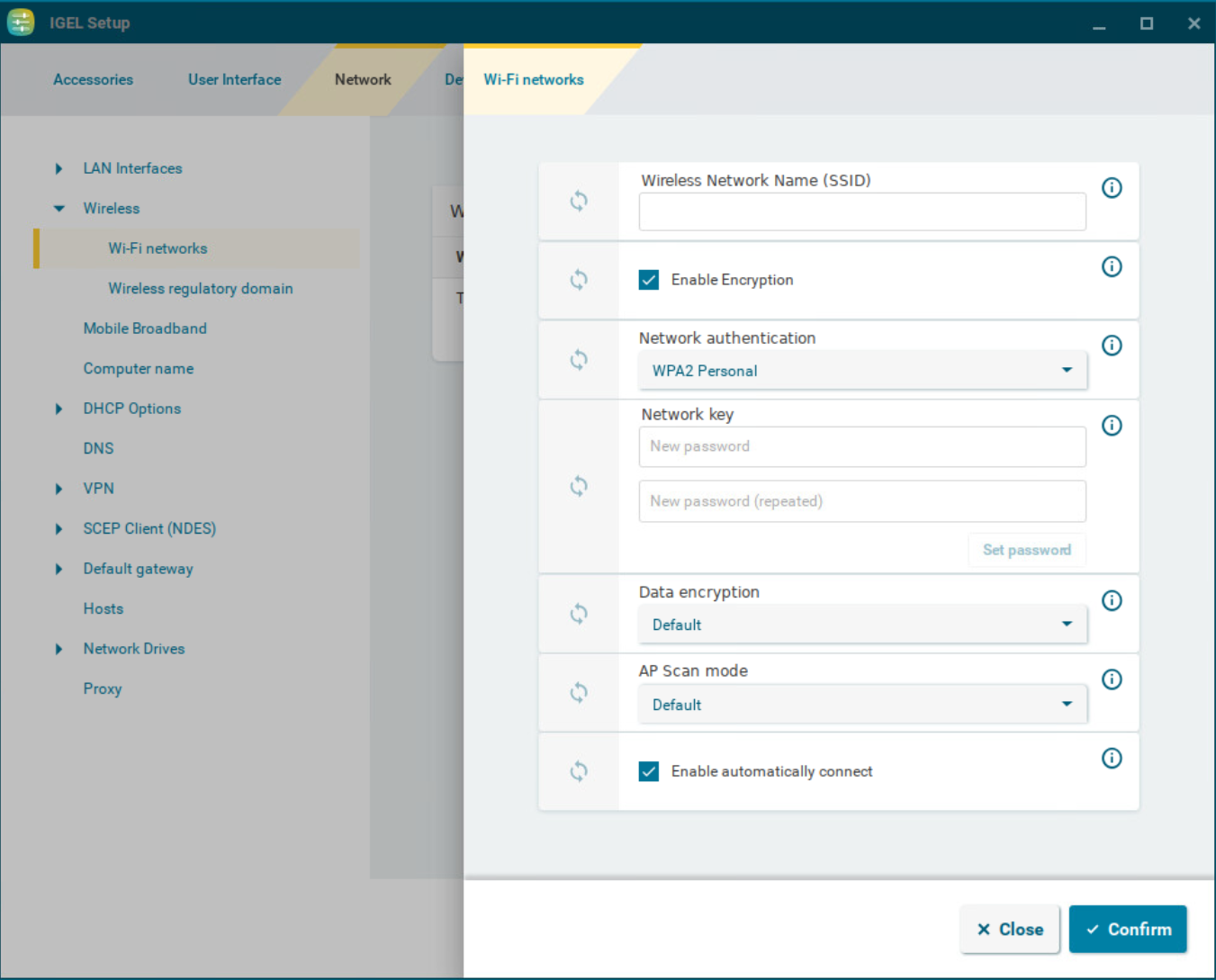
Wireless network name (SSID)
Name of the wireless network (SSID)
Enable encryption
![]() Encrypted connection is used. (Default)
Encrypted connection is used. (Default)
Network authentication
You can configure the following network authentication methods.
- WPA Personal: Wi-Fi Protected Access Pre-Shared Key (WPA / IEEE 802.11i/D3.0)
- WPA2 Personal: Wi-Fi Protected Access Pre-Shared Key (WPA2 / IEEE 802.11i/RSN) (Default)
- WPA3 Personal: Wi-Fi Protected Access SAE (Simultaneous Authentication of Equals)
- WPA Enterprise: Wi-Fi Protected Access with 802.1X authentication (WPA / IEEE 802.11i/D3.0)
- WPA2 Enterprise: Wi-Fi Protected Access with 802.1X authentication (WPA2/IEEE 802.11i/RSN)
Depending on the selection, you can configure the corresponding parameters below.
- For WPA/WPA2/WPA3 Personal encryption, see WPA/WPA2/WPA3 Personal.
- For WPA/WPA2 Enterprise encryption, see WPA/WPA2 Enterprise.
WPA/WPA2/WPA3 Personal Encryption
Network key
WPA network key/passphrase as set at the access point. This is either an ASCII character string with a length of 8...63 or exactly 64 hexadecimal digits.
Data encryption
- Default: The default value depends on which network authentication method is selected. For WPA, TKIP is the default. For WPA2, AES (CCMP) is the default. (Default)
- TKIP: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (IEEE 802.11i/D7.0)
- AES (CCMP): AES in Counter mode with CBC-MAC (RFC 3610, IEEE 802.11i/D7.0)
- AES (CCMP) + TKIP: One of two encryption methods is selected by the access point.
- Automatic: The access point can choose the encryption method freely – nothing is stipulated.
AP scan mode
Scan mode for access points.
- Default (Default)
- Broadcast: Alternative for access points which allow the SSID broadcast
- No broadcast: Alternative for access points which refuse the SSID broadcast (hidden access points)
Enable automatically connect
![]() Automatic connection to the access point is enabled. (Default)
Automatic connection to the access point is enabled. (Default)
WPA/WPA2 Enterprise Encryption
Data encryption
- Default: The default value depends on which network authentication method is selected - TKIP for WPA, AES (CCMP) for WPA2. (Default)
- TKIP: Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (IEEE 802.11i/D7.0)
- AES (CCMP): AES in Counter mode with CBC-MAC (RFC 3610, IEEE 802.11i/D7.0)
- AES (CCMP) + TKIP: One of two encryption methods is selected by the access point.
- Automatic: The access point can choose the encryption method freely – nothing is stipulated.
AP scan mode
Scan mode for access points
- Default (Default)
- Broadcast: Alternative for access points which allow the SSID broadcast
- No broadcast: Alternative for access points which refuse the SSID broadcast (hidden access points)
EAP type
- PEAP: Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol
- TLS: Transport Layer Security with client certificate
- TTLS: Tunneled Transport Layer Security
- FAST: Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling
Anonymous identity
This identity is sent by authentication instead of the actual Identity. This prevents the disclosure of the actual identity of the user. The anonymous identity is relevant for any of the above-mentioned EAP Types, except for TLS.
Auth method
Method for authentication that is available for the selected EAP type.
Possible options:
- MSCHAPv2: Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (Default)
- TLS: Transport Layer Security with client certificate
- GTC: Generic Token Card
- MD5: MD5-Challenge
- PAP: Password Authentication Protocol
Validate server certificate
☑ The endpoint device validates the authenticity of the authentication server against the certificate file. This certificate file is stored under the path defined by CA root certificate.
☐ The authenticity of the authentication server is not validated.
CA root certificate
Path and file name of the file that contains the certificates with which the authentication server authenticates itself.
Identity
User name that is stored at the authentication server
Password
Password relevant to the user name
The following settings are relevant if you have selected TLS as EAP type:
Manage certificates with SCEP (NDES)
☑ Client certificates will automatically be managed with SCEP. For more information on SCEP configuration, see SCEP Client (NDES).
☐ Client certificates will not be managed with SCEP. (Default)
Client certificate
Path to the file with the certificate for client authentication in the PEM (base64) or DER format.
Private key
Path to the file with the private key for the client certificate. The file can be in the PEM (base64), DER, or PKCS#12 (PFX) format. The Private key password may be required for access.
Identity
User name for network access
Private key password
Password for the Private key for the client certificate
The following setting is relevant if you have selected FAST as EAP type:
Automatic PAC provisioning
Specifies how the PAC (Protected Access Credential) is delivered to the client.
Possible options:
- Disabled: PAC files have to be transferred to the device manually, e.g. via UMS file transfer.
- Unauthenticated: An anonymous tunnel will be used for PAC provisioning.
- Authenticated: An authenticated tunnel will be used for PAC provisioning.
- Unrestricted: Both authenticated and unauthenticated PAC provisioning is allowed. PAC files are automatically created after the first successful authentication. (Default)
PAC files are stored in /wfs/eap_fast_pacs/.
PAC file names are automatically derived from the Identity, but are coded. In the case of the manual PAC provisioning, you can determine the PAC file names with the following script: /bin/gen_pac_filename.sh